Can GPS Be Wrong – 11 Reasons Your Tracker Might Be Lying (And How to Fix It)
Your GPS is lying to you. Not always—but more often than you'd think.
One minute, your tracker shows a vehicle parked in the driveway. The next? It’s three blocks away, stuck behind a phantom red light.
So, what the heck is going on?
The secret’s in the signals. Everything from tall buildings to bad weather, even the design of your GPS receiver, can throw off your location. Yes, GPS is smart. But it’s not magic. It relies on satellite signals—and those signals can be blocked, bounced, or weakened in ways that affect GPS accuracy.
Here’s the good news: there are ways to fix it.
In this guide, you’ll learn why GPS tracking devices sometimes get it wrong, what really affects their accuracy, and how to improve GPS performance with a few simple tweaks. We’ll break down complex terms like satellite geometry, multipath error, and cold starts—but in plain English. No tech jargon. No fluff.
You'll walk away knowing:
- What causes tracking errors
- How accurate GPS really is
- Which fixes work (and which are myths)
- And how to get reliable tracking from your device
This isn’t just about theory—it’s about getting the accurate GPS data you need, when it matters most.
Let’s clear up the confusion and get your tracker back on track.
![]()
11 Examples Of What Can Cause GPS Accuracy To Be Wrong
|
Cause |
Description |
|
Signal Blockage |
Obstructions like buildings, forests, or mountains can block signals, causing interference and inaccuracy. |
|
Satellite Geometry |
Poor arrangement of GPS satellites can distort signals and reduce accuracy. |
|
Atmospheric Interference |
Conditions like ionosphere interference can distort signals, leading to inaccuracies. |
|
Receiver Design Features |
Quality and design of the receiver affect accuracy; cheaper receivers may be less accurate. |
|
Multipath Error |
Signals bouncing off surfaces like buildings or trees can cause inaccuracies. |
|
Cold Start |
After being off or in a new location, devices may take time to update, causing inaccuracy. |
|
Software/Firmware Issues |
Outdated or faulty software/firmware can affect accuracy; regular updates and calibration are essential. |
|
Signal Reflection |
Reflection off surfaces like buildings can distort signals, causing inaccuracies. |
|
Time of Signal |
Timing discrepancies in signal reception can affect accuracy. |
|
Weather Conditions |
Poor weather like rain, snow, or fog can cause atmospheric interference, leading to inaccuracies. |
|
GPS Application |
Different applications have varying accuracy levels; some may prioritize battery life over accuracy. |
Signal Blockage
When GPS signals can’t get through buildings, thick forests, or mountains, your tracker might struggle to stay accurate. If you're driving downtown or hiking in the woods, expect some interference.
Satellite Geometry
The way satellites line up at any given time affects GPS accuracy. If they aren’t spaced well in the sky, your GPS might get confused and give a slightly off reading.
Atmospheric Interference
GPS signals travel through the atmosphere, and things like solar activity or interference in the ionosphere can mess with them. It’s like trying to hear someone through static on the radio.
Receiver Design Features
Not all GPS devices are created equal. Cheaper ones might not have the same level of precision as high-quality models. The design makes a difference in how accurately your tracker picks up signals.
Multipath Error
Ever had a GPS tell you you’re somewhere you clearly aren’t? That’s probably multipath error, which happens when signals bounce off buildings or trees before hitting your device.
Cold Start
When you first power up a GPS or move it to a new place, it needs a little time to find its location. Until it updates, the readings might not be spot-on.
Software/Firmware Issues
If the software or firmware on your GPS is outdated or buggy, it can throw off your readings. Keeping your device updated helps it stay reliable and accurate.
Signal Reflection
When GPS signals reflect off glass buildings or smooth surfaces, it can confuse your tracker. This distortion makes it seem like you’re in the wrong spot.
Time of Signal
GPS works on precise timing. If there’s any delay in signal reception, your tracker might get things slightly wrong.
Weather Conditions
Rain, snow, and fog can interfere with GPS signals. When the weather takes a turn, your tracker’s accuracy might dip.
GPS Application
Different GPS systems serve different purposes. Some might focus more on saving battery life, sacrificing a bit of precision. For example, a GPS app for fitness might not be as accurate as one designed for navigation.
Learn more about how GPS tracking works here: https://fleet1st.io/blogs/post/how-gps-works
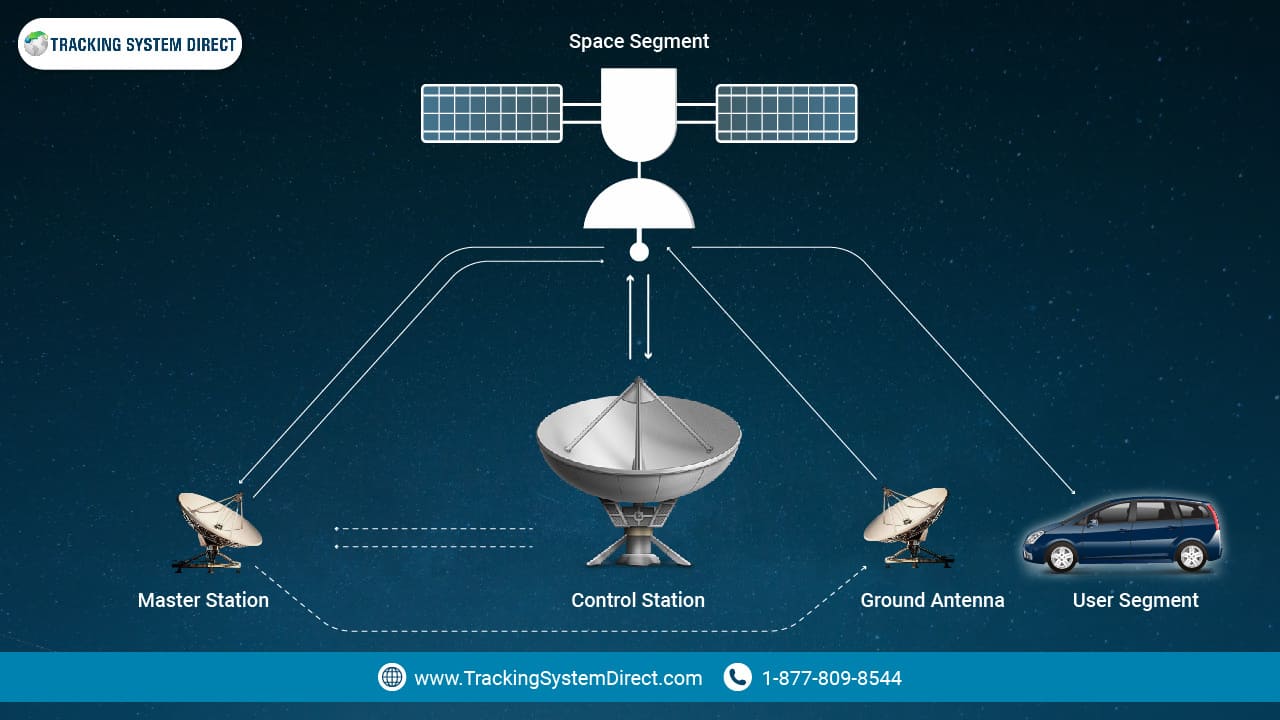
How to Improve GPS Accuracy: Simple Fixes That Make a Big Difference
When your GPS tracker starts acting up—showing you in the wrong spot or lagging behind—don’t panic. GPS accuracy can drift over time, but there are practical ways to improve GPS accuracy and get your location data back on track.
Start Fresh With a Cold Start
Think of this like giving your GPS device a reboot. Over time, your tracker stores satellite info that can get outdated or just plain wrong. Doing a cold start clears out that old data and forces your GPS receiver to reconnect from scratch. That means it can grab fresh info from GPS satellites—a quick and easy way to get more accurate GPS results.
Keep Your Firmware Updated
Your GPS device runs on software that talks to the satellite systems overhead. Manufacturers regularly send out updates that tweak how well your device handles GPS signals, especially in tricky conditions like poor weather or crowded cities. If you want the most accurate GPS possible, make sure your tracker’s firmware and software are up to date.
Boost Signal Strength With an External Antenna
Tall buildings, thick trees, and deep valleys can all mess with your GPS signal strength. This kind of signal blockage can lead to delayed or incorrect tracking. An easy fix? Add an external antenna or amplifier. It helps cut through interference and improves your chances of picking up strong satellite signals, even in tough spots.
Utilize Multiple Satellite Systems for Better Accuracy
If your GPS signal is spotty in areas with limited visibility, consider using multiple satellite systems like GPS and GLONASS. While GPS is the most common, adding systems like GLONASS, BeiDou, or Galileo can help fill in the gaps and give you more precise location data. Using multiple satellite networks boosts your chances of getting an accurate reading, even when one system is blocked or experiencing interference. So, if you want more reliable tracking, connecting to multiple satellite systems is a smart move!

Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, GPS signals can be affected by weather conditions, particularly by atmospheric interference. In general, clear weather conditions with a high visibility are optimal for accurate GPS tracking. However, poor weather conditions, such as heavy rain, snow, or fog, can affect the accuracy of GPS signals.
Yes, tall buildings and other obstacles can interfere with GPS accuracy by blocking or reflecting signals. This is known as the “urban canyon” effect. In cities, try to stay in open spaces and avoid areas with dense trees or tall structures to improve GPS performance.
To keep your GPS system accurate, make sure your firmware and software are up to date. Enable multiple satellite systems, such as GPS, GLONASS, or Galileo, for better coverage. Try to avoid areas with limited satellite visibility, and if needed, use an external antenna or signal booster to strengthen the signal.
No, GPS tracking devices can differ in accuracy depending on the quality of their receiver and the design features of the device. Higher quality GPS receivers tend to provide more accurate results.
GPS trackers are generally very accurate in determining latitude and longitude, with an accuracy range of up to 10 meters. However, factors such as atmospheric interference and satellite geometry can affect accuracy. For more precise results, use multiple satellite systems and check for firmware and software updates regularly.
